Translate this page into:
AIDS-Related Kaposi Sarcoma in a Tertiary University Hospital in Manila, Philippines: A Report of Six Cases
Address for correspondence Lance Isidore G. Catedral, MD, Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Medicine, Philippine General Hospital, University of the Philippines, Manila 1000, Philippines. lancecatedral@gmail.com
This article was originally published by Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Private Ltd. and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
We report six cases of Kaposi sarcoma (KS) seen at the University of the Philippines–Philippine General Hospital, a tertiary university hospital with a 1,500-bed capacity in Manila, from 2017 to February 2020. All cases involved males (21–47 years old) infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Majority came from Metro Manila and had opportunistic infections at the time of KS diagnosis, most commonly pulmonary tuberculosis. Four patients presented with multiple hyperpigmented cutaneous patches. One patient had both cutaneous lesions and necrotic gingival mass. One patient presented with a gastrointestinal mass. One patient underwent systemic chemotherapy (liposomal doxorubicin) but was eventually lost to follow-up. Although considered the most common tumor arising from HIV-infected persons, KS is considered rare in the Philippines. No studies have been undertaken to determine its incidence. However, the incidence may be expected to rise due to the increasing number of Filipinos diagnosed with HIV daily.
Keywords
AIDS
HIV
Kaposi sarcoma
Introduction
Between 2010 and 2018, the Philippines has witnessed an unprecedented 203% increase in the number of newly diagnosed cases of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).1 It is considered the fastest growing HIV epidemic in the Western Pacific.2 Addressing this exponential rise in cases has become a major health priority in the country. Antiretroviral treatments (ARTs) are given for free by the Philippine government, and HIV testing hubs have been instituted across the country.
It is estimated that 77,000 adults and children are living with HIV.1 The national prevalence remains low (0.1%). Of these individuals, only 76% know their status. Less than half (44%) receive ART. Of the 13,000 newly diagnosed cases among adults, 12,000 are men.1
With more people being infected with HIV, especially men having sex with men, the incidence of HIV-associated malignancies, particularly acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related Kaposi sarcoma (KS), is also expected to increase.
AIDS-related KS is a common tumor arising in people living with HIV, but has been historically rare in the Philippines. KS commonly presents as cutaneous lesions, but can involve any site in the body. Due to the use of ART, its incidence has declined in the United States.3 KS is also closely linked to human herpesvirus-8.4
The true prevalence of AIDS-related KS has not been established, and the disease continues to remain rare and underreported in the Philippines.
Here we report six cases of AIDS-related KS seen at the University of the Philippines–Philippine General Hospital, a tertiary national university hospital and an HIV-treatment hub, in Manila, Philippines, from 2017 to February 2020.
Cases of AIDS-Related Kaposi Sarcoma
The patients were initially seen at various points of entry in the hospital, including the surgery outpatient clinic, dermatology outpatient clinic, and the Sagip Clinic, the hospital’s HIV treatment hub. The clinical details are summarized in Table 1.
|
Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Case 5 |
Case 6 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Age (y) |
30 |
47 |
23 |
43 |
29 |
21 |
|
Sex |
Male |
Male |
Male |
Male |
Male |
Male |
|
Presenting symptom of Kaposi sarcoma |
One-month history of gingival mass |
Eight-year history of multiple erythematous and violaceous patches on the face, more prominent on perioral area, and left side of chest |
Violaceous smooth plaque on right elbow |
Multiple papules and plaques on plantar aspects of both feet; similar lesions seen in trunk |
Multiple violaceous and black plaques on the extremities, chest, and abdomen |
Violaceous plaque on the right elbow |
|
Year of Kaposi sarcoma diagnosis |
2017 |
2018 |
2017 |
2017 |
2018 |
2020 |
|
CD4 counts (in cell/mm3) |
Information not available |
100 (June 2017) |
Information not available |
Information not available |
15 (June 2018) |
144 (January 2020) |
|
Number of sexual partners for past 5 y |
3 male sexual partners |
Multiple male and female sexual partners |
8 male sexual partners |
8–9 male sexual partners |
4 male sexual partners |
Multiple male partners |
|
Histopathologic findings |
Gingival mass: Capillary hemangioma |
Chin skin punch biopsy: Kaposi sarcoma - proliferation of narrow, jagged, slit-like mature and immature vessels, proliferation of spindle-shaped cells, presence of siderophages |
Left flank skin punch biopsy: Kaposi sarcoma - proliferation of blood vessels dissecting through collagen bundles with siderophages in the dermis |
Chest skin punch biopsy: Kaposi sarcoma - proliferation of narrow, jagged, slit-like mature and immature vessels, proliferation of spindle-shaped cells, presence of extravasated red blood cells, siderophages |
Forearm skin punch biopsy: Kaposi sarcoma–proliferation of blood vessels and endothelial lining with spindle cell proliferation Gastric mass biopsy: spindle cell proliferation |
Elbow skin punch biopsy: Kaposi sarcoma - proliferation of blood vessels and endothelial lining with spindle cell proliferation |
|
Use of ART at the diagnosis of Kaposi’s sarcoma |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Treatment received for Kaposi sarcoma |
No |
Yes. ART: efavirenz, lamivudine, and tenofovir |
Yes. ART |
Yes. ART: efavirenz, lamivudine, and tenofovir |
Yes. ART and liposomal doxorubicin |
Yes. ART: efavirenz, lamivudine, and tenofovir |
Abbreviations: AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; ART, antiretroviral treatment.
All cases were males (21–47 years old) infected with HIV. Majority had opportunistic infections at the time of KS diagnosis, most commonly pulmonary tuberculosis. Four patients presented with multiple brown, erythematous and violaceous patches and plaques (Fig. 1), while one patient presented with a solitary violaceous plaque on his right elbow. One patient had both cutaneous lesions and necrotic gingival mass. One patient presented with gastrointestinal involvement.
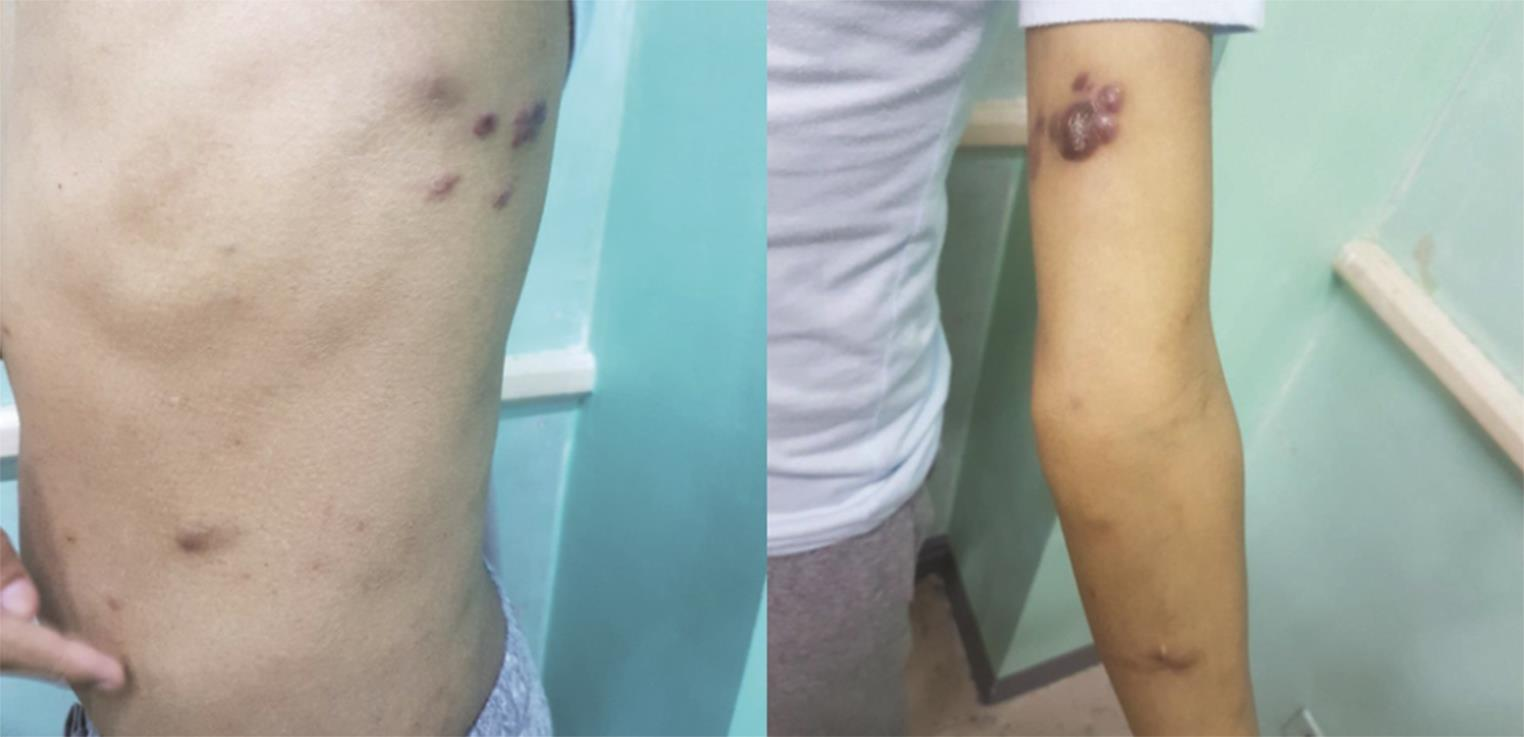
-
Fig. 1 Multiple brown, erythematous and violaceous patches and plaques on the trunk and arms.
Only one patient (case 5) received systemic chemotherapy (liposomal doxorubicin) for visceral involvement. He was able to receive three cycles of chemotherapy, but was eventually lost to follow-up.
Discussion
Although considered the most common HIV-related malignancy, KS is considered rare in the Philippines. Its incidence is currently unknown but is expected to rise due to the increasing number of Filipinos diagnosed with HIV infection daily. It has a variable course, and may present as a minimal disease or as a rapidly progressing neoplasm.
KS can involve any site in the body, but cutaneous disease is the most common presentation. The cutaneous lesions often appear on the lower extremities, face, oral mucosa, and genitalia; the lesions may be mistaken as purpura, hematoma, angiomas, dermatofibromas, or nevi.
KS can also present as a visceral disease5 and usually affects the oral cavity, bone marrow, bone, and skeletal muscle. Visceral involvement has become less common6 likely due to the use of combination ART for HIV.
It is staged using the AIDS Clinical Trails Group staging system of the National Institutes of Health,7 which divides patients into good or poor risk prognostic categories, taking into account the extent of tumor, immune status, and severity of systemic illness.
Goals of treatment are palliation of symptoms, shrinkage of tumor, and prevention of disease progression.8 Virtually all patients with AIDS-related KS are recommended to undergo treatment with combination ART.6,9 Local symptomatic therapy—in the form of intralesional chemotherapy with vinblastine10 or topical alitretinoin11—plays a role in cosmesis and in the management of bulky KS lesions.
Systemic chemotherapy is used with more advanced KS or in cases with rapid disease progression. Accepted indications for the addition of chemotherapy to ART are as follows12:
-
Widespread skin involvement (e.g., more than 25 lesions)
-
Extensive cutaneous KS that is unresponsive to local treatment
-
Extensive edema
-
Symptomatic visceral involvement
-
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
-
Progression of KS on ART alone
If systemic chemotherapy is indicated, the recommended first-line treatment is pegylated liposomal doxorubicin or liposomal daunarubicin.13 Single-agent chemotherapy with paclitaxel, bleomycin, vinblastine, vincristine, and etoposide have also been used.14 In resource-limited settings, paclitaxel with ART is superior to oral etoposide plus ART or etoposide and vincristine plus ART.15
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Francisca Roa and Dr. Arthur Dessi Roman for their technical assistance.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
References
- UNAIDS. Country Factsheets: HIV and AIDS estimates. 2018. Available at: https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/philippines. Accessed March 8, 2020
- Correspondence HIV crisis in the Philippines: urgent. Lancet Public Health. 2019;4(02):e84.
- [Google Scholar]
- Kaposi’s sarcoma among persons with AIDS: a sexually transmitted infection? Lancet. 1990;335:123-128. (8682)
- [Google Scholar]
- Human herpesvirus 8 seropositivity and risk of Kaposi’s sarcoma and other acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related diseases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91(17):1468-1474.
- [Google Scholar]
- Kaposi sarcoma of the musculoskeletal system: a review of 66 patients. Cancer. 2007;109(06):1040-1052.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prospective stage-stratified approach to AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(05):409-414.
- [Google Scholar]
- Kaposi’s sarcoma in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: a proposal for uniform evaluation, response, and staging criteria. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7(09):1201-1207.
- [Google Scholar]
- Management of AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma: advances in target discovery and treatment. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2002;2(02):193-200.
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of severe or progressive Kaposi’s sarcoma in HIV- infected adults. Cochrane Libr (09):1-74.
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of oral Kaposi sarcoma with intralesional vinblastine. Cancer. 1993;71(05):1722-1725.
- [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of AIDS-related cutaneous Kaposi’s sarcoma with topical alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid) gel. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1999;22(03):235-246.
- [Google Scholar]
- AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma: clinical manifestations and diagnosis Waltham, MA: UpToDate; (ed).
- [Google Scholar]
- AIDS Malignancy Subcommittee. British HIV Association guidelines for HIV-associated malignancies 2008. HIV Med. 2008;9(06):336-388.
- [Google Scholar]
- Chemotherapy of AIDS–related Kaposi’s sarcoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1996;10(05):1051-1068.
- [Google Scholar]
- Highly active antiretroviral therapy in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma: implications for the design of therapeutic trials in patients with advanced, symptomatic Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(03):399-402.
- [Google Scholar]







